How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and essential safety regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone components, mastering flight techniques, and understanding the importance of responsible operation.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies with your drone. We’ll delve into practical tips and troubleshooting strategies, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable experience every time you take flight.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the individual parts of your drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key components and provides a glossary of common terms.
Drone Component Functions
Each component plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. Understanding their individual functions allows for better troubleshooting and maintenance.
| Component | Function | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for lift and maneuverability. | Bent or damaged propellers, imbalance. | Inspect for damage, replace if necessary; balance propellers if needed. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, providing the necessary power. | Motor failure, overheating. | Check motor connections, ensure proper cooling. Replace faulty motors. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, responsible for controlling flight stability and responsiveness to pilot inputs. | Firmware issues, sensor malfunctions. | Update firmware, recalibrate sensors. Contact manufacturer for advanced troubleshooting. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Low battery, battery failure, overheating. | Monitor battery levels, use appropriate charger, allow battery to cool before recharging. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data for autonomous flight modes and return-to-home functionality. | Weak GPS signal, inaccurate location data. | Fly in an open area with clear sky view, calibrate GPS. |
| Camera | Captures images and videos. | Lens smudges, malfunctioning image sensor. | Clean the lens, check camera settings. Contact manufacturer for repairs. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Stabilizes the camera, ensuring smooth footage. | Gimbal malfunction, calibration issues. | Recalibrate the gimbal, check for physical damage. |
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms will enhance your understanding of manuals, online resources, and discussions with other drone pilots.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mounting system for the camera.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A function that allows the drone to automatically return to its takeoff point.
- Throttle: Controls the vertical movement of the drone (ascent and descent).
- Yaw: Rotation of the drone around its vertical axis.
- Pitch: Movement of the drone forward or backward.
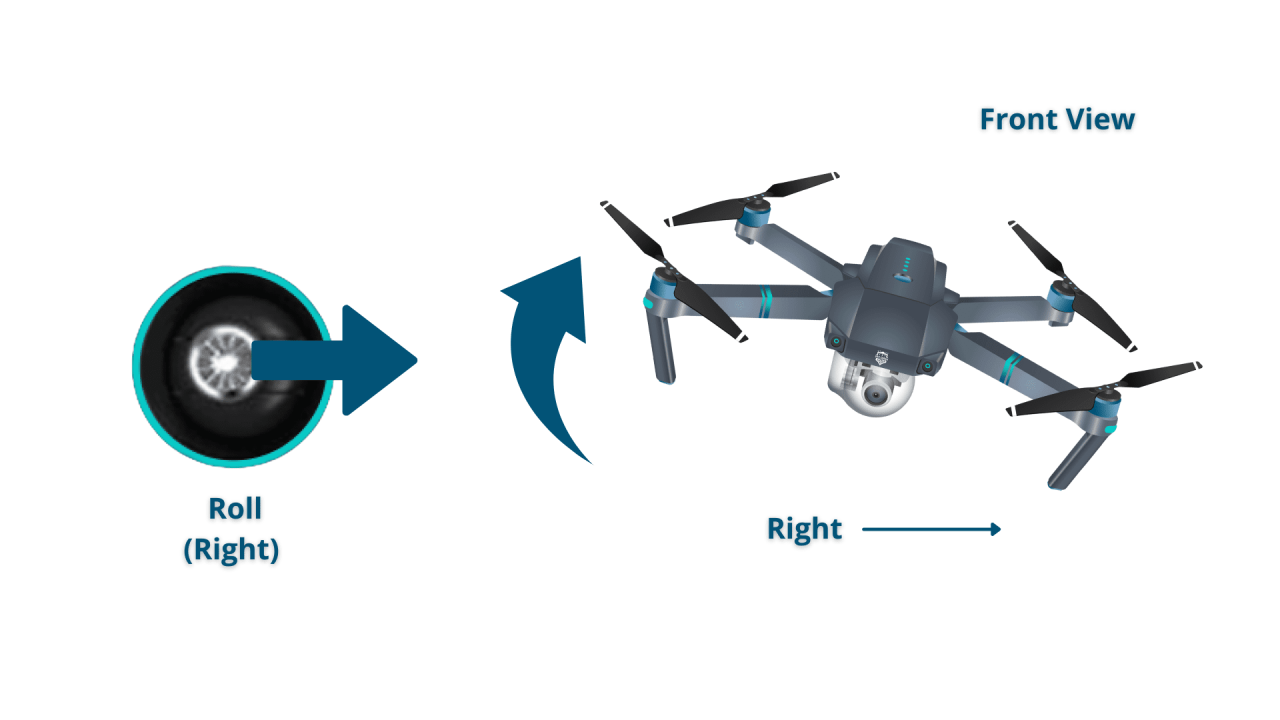
- Roll: Movement of the drone left or right.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and efficient drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
This checklist should be performed before every flight to ensure the drone is in optimal condition.
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the propellers for damage or cracks.
- Verify that all components are securely attached.
- Inspect the battery for any signs of damage or swelling.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is adequately charged.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS.
- Confirm that the flight controller firmware is up-to-date.
- Check the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Review local regulations and restrictions for drone operation.
- Ensure you have sufficient free space around you for flight operations.
Battery Inspection and Charging
Proper battery care is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully.
- Inspect the battery for any signs of damage, such as swelling, cracks, or leaks.
- Avoid overcharging or discharging the battery.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry place when not in use.
- Use the manufacturer’s recommended charger to avoid damage to the battery.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. These procedures minimize the risk of accidents and damage.
Takeoff Techniques
A smooth and controlled takeoff is crucial for safe flight. Proper throttle management prevents abrupt movements and potential crashes.
- Ensure the drone is in a level and stable position.
- Gradually increase the throttle to lift the drone smoothly.
- Maintain a steady ascent rate.
- Avoid sudden movements of the control sticks.
Landing Procedures
A smooth and precise landing ensures the safety of the drone and its surroundings. Wind conditions should always be considered during landing.
- Reduce the throttle gradually to descend smoothly.
- Maintain a steady descent rate.
- Adjust the control sticks to compensate for wind.
- Set the drone down gently on a level surface.
Takeoff and Landing Variations
Different drone models may have slightly different takeoff and landing procedures. Always consult the manufacturer’s manual for specific instructions.
- Some drones offer automated takeoff and landing features.
- Others may require more manual control.
- Always prioritize safety and smooth transitions.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and efficient drone operation. This section details the use of control sticks and common maneuvers.
Control Stick Operation
The control sticks typically control the drone’s movement in six directions: forward, backward, left, right, up, and down.
- Left Stick: Controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right).
- Right Stick: Controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (up/down).
Common Flight Errors and Corrections
Pilots often encounter common flight errors, which can be corrected with practice and understanding.
- Drifting: Caused by wind or improper trim; adjust trim settings or compensate with control sticks.
- Sudden drops: Often due to low battery; monitor battery levels closely.
- Uncontrolled rotations: May indicate a problem with the flight controller; recalibrate or seek professional help.
Basic Maneuvers
Mastering these basic maneuvers will provide a solid foundation for more advanced flight techniques.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Turning: Rotating the drone around its vertical axis (yaw).
- Ascending/Descending: Controlling the drone’s altitude.
- Forward/Backward/Left/Right Movement: Controlling the drone’s horizontal position.
Advanced Flight Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
Advanced flight techniques require practice and skill. This section provides an overview of these techniques and resources for further learning.
Stable Flight in Windy Conditions
Maintaining stable flight in windy conditions requires anticipating wind gusts and making appropriate control adjustments.
- Use a lower throttle to reduce the impact of wind.
- Anticipate wind gusts and make subtle control adjustments.
- Practice flying in different wind conditions to improve your skills.
Complex Maneuvers
More advanced maneuvers require precision and control. Practice is key to mastering these techniques.
- Precise Positioning: Accurately placing the drone in a specific location.
- Smooth Camera Movements: Creating fluid and professional-looking aerial footage.
Resources for Advanced Flight
Numerous resources are available to help pilots learn advanced flight techniques.
- Online tutorials and courses.
- Drone simulator software.
- Local drone clubs and communities.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Understanding your drone’s camera features and settings is essential for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This section explores camera settings and composition techniques.
Camera Settings and Adjustments

Adjusting camera settings allows for creative control over the final image or video.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration of exposure, impacting motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens, affecting depth of field.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light, impacting image noise.
Aerial Shot Composition
Effective composition is crucial for creating visually appealing aerial images and videos.
- Rule of Thirds: Placing key elements off-center for a more balanced composition.
- Leading Lines: Using lines in the scene to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Creating visually appealing compositions using repetitive elements.
Flight Modes and Camera Operation
Different flight modes can significantly impact camera operation and the resulting footage.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety regulations and technical proficiency. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently and safely operate your drone.
- Cinematic Mode: Provides smoother camera movements, ideal for professional-looking footage.
- Sport Mode: Enables faster and more agile flight, but may result in shakier footage.
Battery Management and Flight Time
Proper battery management is essential for maximizing flight time and ensuring the longevity of your drone’s battery. This section discusses monitoring battery levels and extending flight time.
Monitoring Battery Levels
Closely monitoring battery levels during flight is crucial to prevent unexpected power failures.
- Pay attention to the battery level indicator on your drone’s controller or app.
- Plan your flights to allow for a safe return with sufficient battery reserve.
- Avoid pushing the battery to its absolute limit.
Extending Flight Time
Several strategies can help extend your drone’s flight time.
- Optimize Flight Patterns: Avoid aggressive maneuvers that consume more power.
- Minimize Battery Drain: Turn off unnecessary features when not needed.
- Use High-Capacity Batteries: Invest in higher capacity batteries for longer flight times.
Signs of a Failing Battery
Recognizing the signs of a failing battery is essential for preventing potential issues during flight.
- Swelling: A sign of internal damage.
- Reduced Flight Time: A significant decrease in flight time compared to previous flights.
- Overheating: The battery gets excessively hot during charging or flight.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is crucial for responsible drone operation. This section highlights safety hazards, regulations, and guidelines.
Safety Hazards
Several potential hazards are associated with drone operation.
- Loss of Control: Caused by various factors, including wind, battery failure, or pilot error.
- Collisions: With objects or people.
- Propeller Injuries: Keep clear of the propellers while the drone is operating.
Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary depending on location. Always check local laws and regulations before flying.
- Registration requirements: Many countries require drone registration.
- No-fly zones: Restricted airspace near airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas.
- Privacy concerns: Respect people’s privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
Safety Guidelines
Following these guidelines will promote safe and responsible drone operation.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these essentials, including detailed instructions and safety procedures, please refer to this helpful resource on how to operate a drone which offers practical advice for both beginners and experienced pilots.
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for everyone involved.
- Always fly within your visual line of sight.
- Avoid flying near people or crowds.
- Never fly in adverse weather conditions.
- Regularly inspect your drone for damage.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Even with careful operation, drones can experience malfunctions. This section provides troubleshooting steps for common problems.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Several common issues can affect drone performance.
- Motor Failure: A motor may fail due to damage or overheating.
- GPS Issues: Weak GPS signal can lead to inaccurate positioning or loss of control.
- Low Battery: Insufficient battery power can cause unexpected power failure.
Troubleshooting Steps, How to operate a drone
Systematic troubleshooting can often resolve common drone problems.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Prevention Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor Failure | Damage, overheating | Inspect motor, check connections, replace if necessary | Regular inspection, avoid overheating |
| GPS Issues | Weak signal, interference | Fly in open area, recalibrate GPS | Fly in areas with clear sky view |
| Low Battery | Overuse, old battery | Charge battery, consider replacing old battery | Monitor battery levels, use appropriate charger |
| Drone Won’t Connect | Bluetooth/Wi-Fi issues, app problems | Check device connections, restart drone/app, update firmware | Ensure strong signal, regular app updates |
| Unstable Flight | Wind, sensor issues | Fly in calm conditions, recalibrate sensors | Avoid windy conditions, regular calibration |
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and cleaning procedures.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures your drone remains in top working order.
- Weekly Inspection: Check for physical damage, loose parts, and battery condition.
- Monthly Cleaning: Clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens.
- Quarterly Checkup: More thorough inspection of all components and firmware updates.
Cleaning Procedures
Proper cleaning techniques prevent damage to delicate components.
- Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the drone body.
- Gently clean the propellers with a soft brush.
- Clean the camera lens with a lens cleaning solution and a microfiber cloth.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
Safe Storage

Proper storage protects your drone from damage and extends its lifespan.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Store the battery separately from the drone.
- Use a protective case to prevent damage during transport.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical understanding, practical skill, and a commitment to safety. From understanding your drone’s components to navigating complex flight maneuvers, this guide has provided a structured pathway to becoming a proficient drone pilot. Remember, consistent practice and adherence to safety regulations are key to unlocking the full potential of your drone and enjoying the unparalleled perspectives it offers.
FAQ Section
What is the legal age to operate a drone?
The legal age varies by country and even by specific drone regulations. Check your local aviation authority for specific age limits.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’ve transported your drone or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to manual control and attempt a controlled landing. Prioritize safety and avoid flying in areas where GPS loss is likely.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by region. Check with your local aviation authority to determine if registration is mandatory and how to complete the process.
